Last review: January, 2026
Banobras offers interested parties information on the sector in Mexico with data from various sources in order to provide knowledge on the subject and useful elements for decision-making at the sectoral level. The content presented does not reflect the position of Banobras.
DOF: Environment and Natural Resources Sector Program 2025–2030. View document
SEDEMA: Zero Waste – Mexico City moves towards a circular economy (August 28, 2025). View document
Current status
Based on the provisions of the General Law for the Prevention and Comprehensive Management of Waste (LGPGIR; DOF, 2003), waste is formally defined as materials or products that are discarded, whether in solid, semi-solid, liquid, or gaseous states, contained in containers or deposits, and that require treatment or final disposal.
They are classified according to their characteristics and origins into three groups:
- Urban solid waste (RSU)
- Special handling waste (RME)
- Hazardous waste (RP)
Urban solid waste (RSU) refers to waste produced in residences, including homes, offices, or small businesses, as well as waste generated from any other activity conducted in establishments or on public streets, with residential characteristics, and waste produced in public places, as long as it is not classified as waste of another type.
Municipalities are responsible for the comprehensive management of RSU, which includes collection, transportation, treatment, and final disposal. However, this process involves a network of key actors playing fundamental roles throughout the system.

Source: Solid Waste, Ministry of the Environment, 2024.
The Ministry of Environment and Natural Resources (SEMARNAT) plays a crucial role by establishing guidelines and regulations for the proper management of urban waste. Additionally, various governmental and private entities have specific responsibilities and functions, all aimed at protecting the environment, public health, and promoting practices that foster a circular economy, thereby reducing environmental impact.
According to the document “Basic Diagnosis for Comprehensive Waste Management 2020” by SEMARNAT, the per capita generation of solid waste in the country was calculated at 0.944 kg/person/day, with a total waste generation estimated at 120,128 tons/day.
The composition of waste at the national level is divided into three main categories:
- Recoverable (31.55%)
- Organic (46.42%)
- Other (22.03%)
These percentages vary by region and municipal population; less populated municipalities generate more organic waste, while more densely populated areas produce a greater amount of recoverable waste.
According to the National Institute of Ecology and Climate Change (INECC), having adequate infrastructure to treat, recover, and valorize these three categories is essential for building a circular economy. Mitigating the negative externalities they generate is key to promoting sustainable development and reducing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, which in 2019 accounted for 7.37% of total emissions.
Furthermore, the solid waste management infrastructure in Mexico, coordinated by SEMARNAT, is structured as follows:
Collection
The initial process in the comprehensive management of municipal solid waste (MSW) is collection. A total of 16,615 vehicles are available, with a national coverage of 83.87%. In 179 municipalities—equivalent to 0.52% of the national population—waste collection services are not provided, mainly in the states of Chiapas, Oaxaca, Puebla, and Veracruz.[1]
During 2022, the average daily amount of MSW collected in Mexico was 108,146 tons (t), of which 66.7% was through door-to-door collection; 24.9% at designated collection points; and 8.4% through container systems.[2]
Waste Transfer
The second stage involves waste transfer. In Mexico, there are 132 transfer stations located across 123 municipalities. Of these, 71 are used exclusively to transfer waste from collection vehicles to higher-capacity vehicles, either to final disposal sites (FDS) or to other stations. In addition, 24 stations carry out waste compaction processes, while 37 conduct separation processes.[3]
Collection Centers
Collection centers are facilities operated and managed by the municipal government or territorial jurisdiction, aimed at receiving specific materials from the population to ensure proper confinement or channel them into recycling processes.
In 2022, out of the 2,475 municipalities and territorial jurisdictions in the country, 62 reported having collection centers for recyclable materials (2.5%). Within them, 874 facilities were registered, mainly concentrated in Mexico City, Querétaro, Aguascalientes, and Jalisco. These entities, together, reported 805 collection centers for recyclable materials (92.1%).[4]
Treatment Plants
The next stage involves treatment plants. An MSW treatment plant refers to a site or facility where waste treatment processes are carried out to transform their characteristics, with the aim of obtaining useful materials, generating energy, or facilitating their transport, recovery, or final disposal.
Nationwide, there are 48 plants located in 19 states. These facilities focus on various processes, including separation (38%), shredding (6%), compaction (20%), composting (27%), anaerobic digestion (8%), and other processes (1%). These plants treat only 7.45% of the waste generated.
In 2022, the average daily amount of waste sent to treatment plants was 5,661 t, of which an average of 2,394 t per day was recovered, representing 42.3%.[5]
Final Disposal Sites
Finally, final disposal sites are those where waste is permanently confined. In 2022, a total of 2,250 final disposal sites were registered nationwide. Oaxaca had the highest number, with 432 in total.
Taken together, each of these components plays a specific role in Mexico’s integrated waste management network, with the goal of minimizing environmental impact and promoting sustainable practices throughout the country.
Waste management stands as a global challenge that encompasses diverse realities and approaches worldwide. Strategies and outcomes in waste administration differ significantly across regions, highlighting the influence of social, economic, and environmental factors.[6]
[1] SEMARNAT, Basic Diagnosis for the Comprehensive Management of Waste, 2020.
[2] INEGI, Statistics on the Occasion of World Environment Day, 2025.
[3] Ibid.
[4] Ibid.
[5] Ibid.
[6] Ibid.
Institutional Arrangement
In terms of infrastructure, Mexico has a defined strategy that offers investors medium and long-term visibility regarding the development of projects, through a series of plans and programs of national and sectorial scope. To access the information, please consult the following documents:
Sectoral Environment and Natural Resources Program 2025-2030
Organizational Structure
Description of the hierarchy and roles of the different entities and actors involved in the sector, including how the different institutions and agencies coordinate and collaborate.
The Ministry of Environment and Natural Resources (SEMARNAT), through the Directorate of Environmental Promotion and Tourism, is the Federal Government agency responsible for integrating criteria and instruments into various sectors of society and public functions to ensure the optimal protection, conservation, and sustainable use of the country’s natural resources. This forms an inclusive and comprehensive environmental policy that aims to achieve sustainable development. SEMARNAT is responsible for establishing the official standards that regulate this activity. In this regard, the National Institute of Ecology and Climate Change (INECC) also plays an important role at the federal level concerning urban solid waste.
An agency dependent on SEMARNAT responsible for generating and integrating technical and scientific knowledge, and enhancing qualified human capital for the formulation, implementation, and evaluation of public policies aimed at protecting the environment, ecological preservation and restoration, low-carbon development, as well as mitigation and adaptation to climate change in the country.
- State Environmental Secretariats or Their Equivalents
States are responsible for ensuring compliance with environmental standards promoted by SEMARNAT to create a conducive environment for ecological development in their communities, in coordination with municipal waste collection and separation agencies. In some cases, the agency responsible for supervising proper solid waste management may be part of the Secretariat of Public Works or the Secretariat of Economic Development, among others.
- Decentralized Public Organizations (OPD)
Some states lack Secretariats of Environment or equivalent agencies, and therefore may have Decentralized Public Organizations.
- State Prosecutor’s Offices
These offices are responsible for reviewing and regulating the final disposal of waste and ensuring that confinement sites operate in accordance with the standards established by SEMARNAT (NOM-083), the General Law for the Prevention and Comprehensive Management of Waste (LGPGIR), and environmental impact issues.
Local Directories
Municipalities are responsible for ensuring compliance with environmental standards promoted by SEMARNAT to create a conducive environment for ecological development in their communities. They also implement solid waste separation programs under the powers granted by Article 115 of the Constitution regarding urban solid waste and the General Law for the Prevention and Comprehensive Management of Waste (LGPGIR).
This is a coordination mechanism for the development of infrastructure in the sectors of communications, transportation, water, environment, and tourism. It holds concessions for 50 highway segments, and with these fees, it finances new infrastructure.
FONADIN-PRORESOL
Within the sectoral programs of FONADIN is the Municipal Solid Waste Program (PRORESOL), which supports local and federal governments, as well as agencies at different levels of government, in structuring and financing solid waste management projects, preferably through a public-private partnership (PPP) scheme.
This is a Mexican development bank institution that enables the development of infrastructure projects with high social profitability by financing long-term projects and promoting the participation of the private sector and commercial banks.
Legal system
The compilation of international treaties, laws, regulations, decrees, agreements and federal, state and municipal provisions shown here are for informational purposes and for ease of reference:
SEMARNAT / CONAGUA
Public Works and Related Services Law

Investment cycle
The following section provides an overview of the project development process from initial planning to final execution.
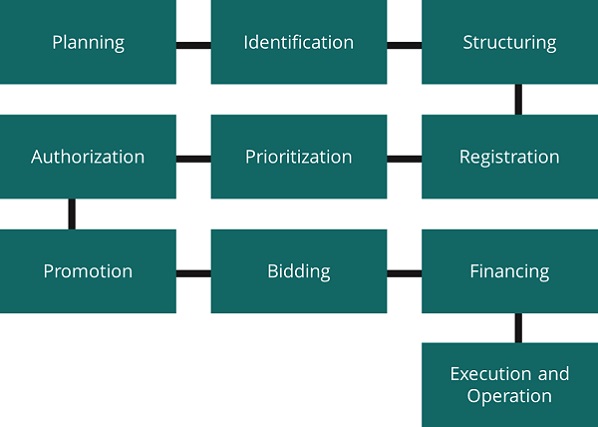
Planning
The planning for the management and implementation of urban, special and hazardous solid waste management policies falls on the municipalities, states and the Federal Government respectively, following the norms and guidelines established by SEMARNAT as well as the National Program for the Prevention and Comprehensive Management of Waste (PNPGIR), and the National Program for the Prevention and Comprehensive Management of Special Management Waste (PNPGIRME) based on the Basic Diagnosis for Comprehensive Waste Management (DBGIR).
* the PNPGIRME is currently in preparation
Identification
The municipalities, through a municipal program for the prevention and comprehensive management of waste, are in charge of identifying the infrastructure needs in the management of solid waste, as well as the state and federal governments are in charge of special and hazardous waste management respectively.
Structuring
The agencies in charge of environmental matters in each municipality, as well as state and federal agencies, are in charge of carrying out the studies and analyses necessary for the development of the projects. Likewise, FONADIN through PRORESOL supports the structuring. The different multilateral organizations also support the structuring of projects.
Registration
The agencies and/or secretariats in charge of solid waste in municipalities and states are responsible for keeping a record of their solid waste management projects on their state platforms. In the case of hazardous waste projects, it is up to the promoting agency to register them in the portfolio of the Investment Unit in case of requiring federal and/or FONADIN public resources. When a local or state level project is structured with the help from FONADIN, it should also be registered in the Investment Unit and follow federal laws.
Priorization
The states and municipalities are in charge of carrying out the prioritization of projects according to their needs, which are reflected in their State Development Plans, the PEPGIR and in turn in the PMPGIR, in terms of urban solid waste. In the case of federal projects, these must be analyzed by the Intersecretarial Commission for Public Expenditure, Financing and Disincorporation (CIGFD), who determines their relationship for their inclusion in the Federal Budget Expenditures (PEF).
Autorization
Projects with PEF resources are authorized by Congress. FONADIN PRORESOL projects are authorized by the Evaluation and Financing Subcommittee of FONADIN and FONADIN’s Technical Committee. Municipal and state projects are authorized by their councils and local congresses.
Promotion
The municipalities and states are in charge of carrying out the promotion of their projects. In certain projects, SEMARNAT as well as the Welfare Secretariat support the promotion.
Bidding
It is the responsibility of the states and municipalities to host their bidding process through their platforms and processes, always following the established guidelines. When studies and/or projects are supported by FONADIN, bids must be made under federal laws, as well as hosting the bidding process on CompraNet.
Financing
There are various sources of financing, depending on the characteristics of the projects, with state and municipal budgets and allocations being the most popular. Likewise, they can be financed through development banks, multilateral organizations, and FONADIN, which is the only source of public financing for solid waste. For its part, the Federation Expenditure Budget (PEF) supports Solid Waste matters through subsidies.
Execution/Operation
It is carried out by municipal, state and private operators, depending on the type of project and the terms of the contract, following the corresponding environmental guidelines.
Projects
Information on new projects (pre-investment, bidding and execution) within the Mexico Projects Hub platform, which at some stage of the project were considered investment opportunities and do not necessarily have Banobras / Fonadin participation.
New Projects
| Proyect | Sector | Subsector | Stage | Sustainability | Ally Networks |
| 0946 Solid Waste Separation and Processing Plant in Chihuahua | Water and Environment | Solid Waste | Preinvestment | No | No |
No projects found.
Banobras / Fonadin
Financing for States, Municipalities, and Decentralized Public Organizations: Banobras addresses the infrastructure needs of states, municipalities, and their decentralized public organizations.

Technical Assistance to States, Municipalities, and Their Organizations: This involves training, workshops, and advisory services for public administration officials aimed at strengthening their management and revenue collection capabilities, as well as project evaluation.
Directory: Promotion Offices
Project Development: Banobras offers services aimed at assisting public sector agencies and entities in the development of infrastructure projects.
Financial structuring of the project:
- Elaborate and/or update studies required by the Public-Private Partnerships Law.
- Support in the review of the bidding conditions and contract model.
- Assist in obtaining financing for the project.
- Assist in the registration process of the project in the portfolio of the Investment Unit of the Ministry of Finance and Public Credit (SHCP).
- Assist in dealing with any observations made by the SHCP Investment Unit.
- Support in the financial closing of the project.
Municipal Solid Waste Program(Proresol)
PRORESOL is the strategy of the National Infrastructure Fund (FONADIN) and the Ministry of Environment (SEMARNAT) through which non-recoverable supports are allocated for the partial financing of studies and projects aimed at ensuring comprehensive solid waste management. Its operations are governed by the Policies, Bases, and Guidelines on Public Works and Related Services of the National Infrastructure Fund, ensuring transparency and efficiency at every stage.

This program allocates financial support for the development of studies and projects related to Urban Solid Waste (RSU). Its objective is to encourage the development of projects under public-private partnership schemes that promote the circular economy vision proposed by the Ministry of Environment and Natural Resources (SEMARNAT) in the context of comprehensive management of urban solid waste and special handling.
Contact: fonadin.medioambiente@banobras.gob.mx
Banobras and International Financial Institutions
Non-Reimbursable Financing Agreement for Investment from the Global Environment Facility (GEF)
The Non-Reimbursable Financing Agreement for Investment from the Global Environment Facility (GEF), aims to strengthen climate change mitigation and adaptation capacities in three Mexican cities (Xalapa, Veracruz; La Paz, Baja California Sur; and San Francisco de Campeche, Campeche), through the preparation and execution of priority projects of the Emerging and Sustainable Cities Program (ESCP) of the Inter-American Development Bank, in the clean energy, solid waste management, and sanitation sectors.
Contact: contacto.banobras@banobras.gob.mx
Sustainability
Banobras makes available to interested parties, analysis sheets for the detection of sustainability practices in infrastructure projects, in accordance with the methodological framework “Attributes and Framework for Sustainable Infrastructure” of the Inter-American Development Bank (IDB). Its objective is to highlight sustainable practices, encourage their adoption in future projects and provide relevant information for investors in their economic, environmental, social and institutional dimensions.
To consult the projects that already have a sustainability record, select the “SEARCH CRITERIA>” option in the PROJECTS section, and then select “With Sustainability Analysis”; the projects that have a record will be displayed below.
In addition, Banobras offers an analysis tool that presents the potential relationship of the different infrastructure projects of the Mexico Projects platform with the 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) of the 2030 Agenda and their targets. This comparative analysis facilitates the use of data according to different criteria, such as the potential impact of projects and sectors against national and global development goals.
The comparison is only made between projects in the same subsector. To select and consult here.
The alignment of a project with the SDGs provides information on the degree of focus on sustainability; it provides a comparison between projects in the same sector and sub-sector and facilitates investment decisions, showing the highest and lowest alignment of projects to the SDGs. Comparative analysis facilitates the use of data according to different criteria, such as the potential impact of projects and sectors against national and global development goals.
In the case of the sector, 1 project is identified in the platform that have sustainability practices detection sheets, which allows to know, among other things, the projects with more and better alignments to the SDGs. For more information, access the Sustainable Development Goals application:
Greater alignment of the sector:
- SDG 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
- SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
- SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
Reduced alignment of the sector:
- SDG 2: Zero Hunger
- SDG 4: Quality Education
- SDG 5: Gender Equality
- SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation
- SDG 10: Reduced Inequalities
- SDG 14: Life Below Water
Ally Networks
Banobras, through its Ally Networks application, provides information on companies participating in competitive public procurement processes for infrastructure projects in Mexico, based on official sources such as ComprasMX. It includes details on investment amounts, number of participations in bids, projects awarded, consortiums, and business associations, which allows the user to identify potential actors for the establishment of investments in the country.
To consult the projects that have information on the participating companies, select the option “SEARCH CRITERIA>” in the PROJECTS section, and then select “With applicant companies” at the end of the criteria.
Reference documents:
This section offers documents, reports and reports with technical, statistical and regulatory information on the sector:
Official Statements:
2025
- 10/20/2025 SEMARNAT: Update of the National Climate Change Strategy.
- 09/08/2025 DOF: Environment and Natural Resources Sector Program 2025–2030.
- 08/28/2025 SEDEMA: Zero Waste – Mexico City moves towards a circular economy.
- 06/03/2025 INEGI: Statistics on the Occasion of World Environment Day.
- 05/08/2025 DOF: AGREEMENT delegating powers to the head of the Undersecretariat of Communications and Transport of the Ministry of Infrastructure, Communications and Transport.
- 04/15/2025 SICT: Undersecretariat of Communications and Transportation to Receive New Powers in Urban Infrastructure and Waste Management.





