Last review date: May, 2024
Ideal location for business
Mexico is the 5th largest country in the Americas and the 14th largest country in the world, with a total area of almost 2 million square kilometers.[1] Mexico has a privileged location as the heart of the Americas: geographically, it is part of North America, but its language, historical roots and culture make it part of Latin America. Moreover, its long coastline makes Mexico a natural bridge between the Atlantic and the Asia-Pacific region. The country is characterized by its natural resources richness, mostly necessary for the productive development of any country. Politically, Mexico is a representative, democratic and federal republic with a territory divided in 32 federal entities and 2,475 municipalities.[2]
[1] Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Geografía (INEGI), Mexican Territory.
[2] Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Geografía (INEGI), Mexican Territory.
Territory, Location and Borders
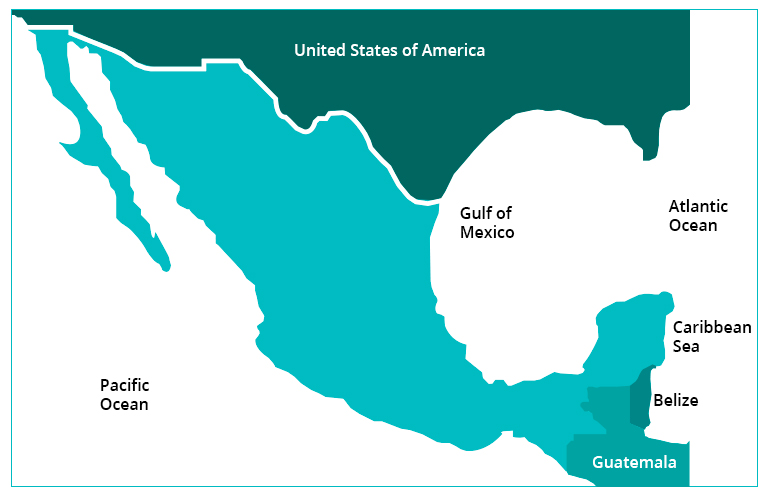

Coast Line
13th
coast line extension
worldwide
More than 11,000 km of coastline divided between the Atlantic coast with 3,294 km (Gulf of Mexico and Caribbean Sea) and the Pacific coast with 7,728 km place Mexico in a strategic position,[1] facilitating access to major consumption hubs worldwide. As a result, companies operating in the country may respond faster, reducing logistic and inventory costs.
[1] Secretaría de Medio Ambiente y Recursos Naturales, Mexican Coastline.
Mexico has a 3,152 km borderline with the United States of America. Likewise, and average of over one million people, 300 thousand vehicles and 70,000 trucks cross this border daily through 56 international crossings.[2] 26.1% of Mexico’s GDP is generated in the border region, while the economic activity of the ten border states of both countries (California, Arizona, New Mexico, Texas in the USA, and Baja California, Sonora, Chihuahua, Coahuila, Nuevo Leon and Tamaulipas in Mexico) would represent the 3rd economy worldwide.[3]
To the South, the country shares a border of 956 km with Guatemala and 193 km with Belize (does not include 85.266 km of maritime boundary in Chetumal Bay), with eight border crossings with Guatemala and one with Belice, that represent the entrance to Central America, the Caribbean and South America.[4]
[2] Secretaría de Relaciones Exteriores, [2024].
[3] Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Geografía (INEGI), [2024].
[4] Secretaría de Relaciones Exteriores, [2024].
Blocs and Regional Integration
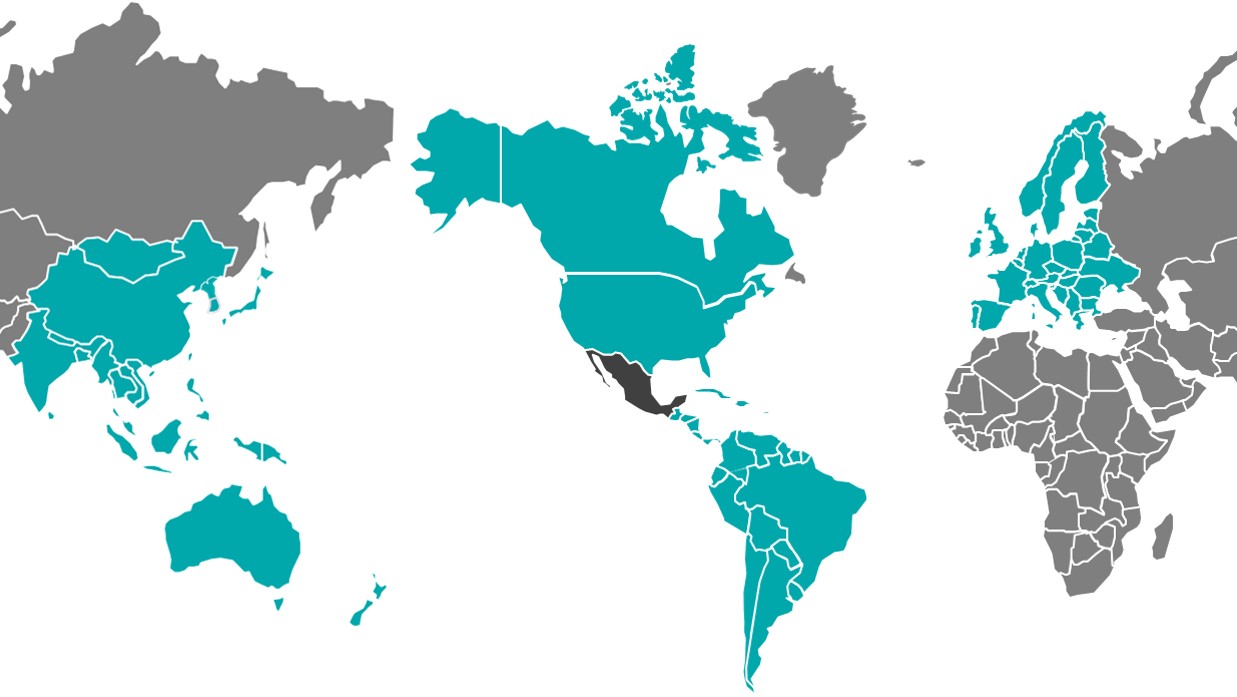
Latin America
Mexico is also part of Latin America, a region formed by countries of similar historical roots and cultures. Although the economic growth of this region has been limited by a volatile international environment, the individual economic performance of these countries is heterogeneous and, in general, is characterized by a constant development. Recently, Mexico promoted a regional integration initiative with Chile, Colombia and Peru, known as the Pacific Alliance, to create a commercial bloc representing Latin America’s 41% of GDP, 59% of total trade and 44% of total foreign investment in Latin America.[1] This initiative holds paramount relevance, considering it would represent the 8th economic power in the world.
[1] World Economic Outlook Database, International Monetary Fund, [2024].
Europe
Europe has a population of more than 447 million people with a GDP per capita of USD 39,940[1] among the highest in the world, that combined with its commercial dynamism, makes it one of the most important markets worldwide. Mexico signed a free trade agreement with the European Union that is in force since 2000, and offers preferential access and protection to its 27 member countries in both, commercial and investment matters.
As part of the United Kingdom´s transitions with the European Union, an agreement was signed between Mexico and the United Kingdom that will maintain preferential access to trade, which entered into force on january 1st, 2021 and is subject to parliamentary procedures and legistlative approvals.
[1] International Monetary Fund, [2023].
North America
Mexico, the United States of America, and Canada integrate the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), the largest economic bloc, with an aggregate GDP that represent 29.89% of the gross world product.[1]
On November 30th, 2018, the three countries signed the US-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA), which represents a modernization of NAFTA, and have come into effect 1st of july 2020.
[1] International Monetary Fund, [2023].
Asia – Oceania
The Asia-Oceania Region is formed by more than 50 economies with an important economic growth; with a population of more than 4,7 billions, accounts for more than 62.9% of the world’s total population, and its economy represents 36% of the gross world product, and 36% of total global trade.[1] In March of 2018 Mexico and 10 other countries signed the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP), one of the most relevant agreements due to its economic and regional influence (Asia, Oceania, North America and South America), and the variety of addressed subjects.
[1] UNESCAP [2023], World Economic Outlook Database, International Monetary Fund, [2024], World Bank, 2024.
Natural Resources
Geographic location, topography and weather diversity make Mexico the 4th biodiverse country, with 9 of the 11 different types of ecosystems, around 200,000 different species, and home to approximately 12% of worldwide biodiversity.[1]
As a consequence, Mexico has important natural resources that contribute to the development of productive and industrial activities.
[1] Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Geografía (INEGI), Mexican Territory.
Political Division
Mexico is a democratic republic, divided in states, united by a federal pact. The states or federal entities are free, sovereign, autonomous and independent among each other, and are governed according to their own legislation, which is defined in local constitutions. Each legislation is governed by the principle of non-competition in national affairs, in accordance with the Constitution of the United Mexican States. Despite their autonomy, the states are not allowed to make alliances with other states or countries without the Federal Government’s approval.
The 32 states that form the Mexican Republic are divided in 2,475 municipalities, representing the basis of the territorial structure.
Aguascalientes
| Number of Municipalities | % of GDP | % of Population |
| 11 | 1.3 | 1.13 |
Baja California
| Number of Municipalities | % of GDP | % of Population |
| 7 | 3.9 | 2.99 |
Baja California Sur
| Number of Municipalities | % of GDP | % of Population |
| 5 | 0.7 | 0.63 |
Campeche
| Number of Municipalities | % of GDP | % of Population |
| 13 | 1.7 | 0.74 |
Coahuila
| Number of Municipalities | % of GDP | % of Population |
| 38 | 3.53 | 2.50 |
Colima
| Number of Municipalities | % of GDP | % of Population |
| 10 | 0.6 | 0.58 |
Chiapas
| Number of Municipalities | % of GDP | % of Population |
| 124 | 1.5 | 4.40 |
Chihuahua
| Number of Municipalities | % of GDP | % of Population |
| 67 | 3.8 | 2.97 |
Ciudad de México
| Number of Municipalities | % of GDP | % of Population |
| 16 | 14.6 | 7.31 |
Durango
| Number of Municipalities | % of GDP | % of Population |
| 39 | 1.15 | 1.45 |
Guanajuato
| Number of Municipalities | % of GDP | % of Population |
| 46 | 4.7 | 4.89 |
Guerrero
| Number of Municipalities | % of GDP | % of Population |
| 85 | 1.3 | 2.81 |
Hidalgo
| Number of Municipalities | % of GDP | % of Population |
| 84 | 1.7 | 2.45 |
Jalisco
| Number of Municipalities | % of GDP | % of Population |
| 125 | 7.5 | 6.62 |
Mexico
| Number of Municipalities | % of GDP | % of Population |
| 125 | 9.0 | 13.48 |
Michoacan
| Number of Municipalities | % of GDP | % of Population |
| 113 | 2.42 | 3.77 |
Morelos
| Number of Municipalities | % of GDP | % of Population |
| 36 | 1.1 | 1.56 |
Nayarit
| Number of Municipalities | % of GDP | % of Population |
| 20 | 0.7 | 0.98 |
Nuevo Leon
| Number of Municipalities | % of GDP | % of Population |
| 51 | 8.0 | 4.59 |
Oaxaca
| Number of Municipalities | % of GDP | % of Population |
| 570 | 1.43 | 3.32 |
Puebla
| Number of Municipalities | % of GDP | % of Population |
| 217 | 3.4 | 5.22 |
Queretaro
| Number of Municipalities | % of GDP | % of Population |
| 18 | 2.4 | 1.88 |
Quintana Roo
| Number of Municipalities | % of GDP | % of Population |
| 11 | 1.5 | 1.47 |
San Luis Potosi
| Number of Municipalities | % of GDP | % of Population |
| 58 | 2.4 | 2.24 |
Sinaloa
| Number of Municipalities | % of GDP | % of Population |
| 18 | 2.2 | 2.40 |
Sonora
| Number of Municipalities | % of GDP | % of Population |
| 72 | 3.5 | 2.34 |
Tabasco
| Number of Municipalities | % of GDP | % of Population |
| 17 | 2.4 | 1.91 |
Tamaulipas
| Number of Municipalities | % of GDP | % of Population |
| 43 | 3.0 | 2.80 |
Tlaxcala
| Number of Municipalities | % of GDP | % of Population |
| 60 | 0.6 | 1.07 |
Veracruz
| Number of Municipalities | % of GDP | % of Population |
| 212 | 4.2 | 6.40 |
Yucatan
| Number of Municipalities | % of GDP | % of Population |
| 106 | 1.6 | 1.84 |
Zacatecas
| Number of Municipalities | % of GDP | % of Population |
| 58 | 1.0 | 1.29 |
Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Geografía (INEGI), 2023.
Levels of Government
First level of government responsible for the maintenance and control of the Mexican Republic. Through the Federation, states activities are regulated and national sovereignty is practiced. Divided in three powers: 1) Executive, represented by the President and Secretaries of State; 2) Legislative, represented by the House of Representatives and the Senate; and 3) Judicial, exercised by the Supreme Court of Justice and the Electoral Court.[1]
[1] Political Constitution of the United Mexican States.
Second level of government derived from a territorial delimitation, with political autonomy, that allows the development of laws and regulations in order to keep social, political, economic, and environmental order in each federal entity. Regulated by the Federal Government, it is responsible to comply with national laws. Divided in three powers: 1) Executive, represented by the State Governor; 2) Legislative, represented by local representatives; and 3) Judicial, represented by the State Supreme Court.[1]
[1] Political Constitution of the United Mexican States.
Third level of government based on territorial delimitation of each state. Each municipality is governed by a council elected by the people and is represented by a mayor. Municipalities are responsible for providing basic utilities to its inhabitants. Prior authorization of the city council, municipalities are allowed to coordinate and associate to render better public services.[1]


